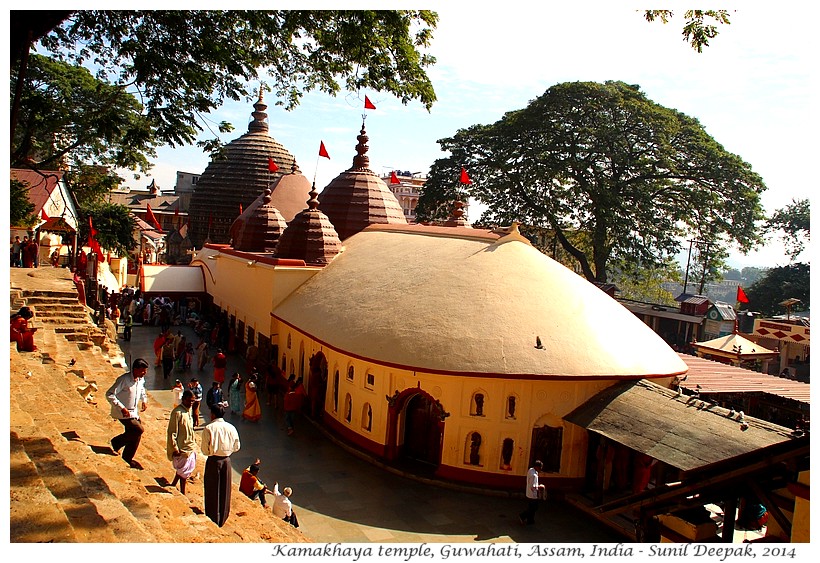
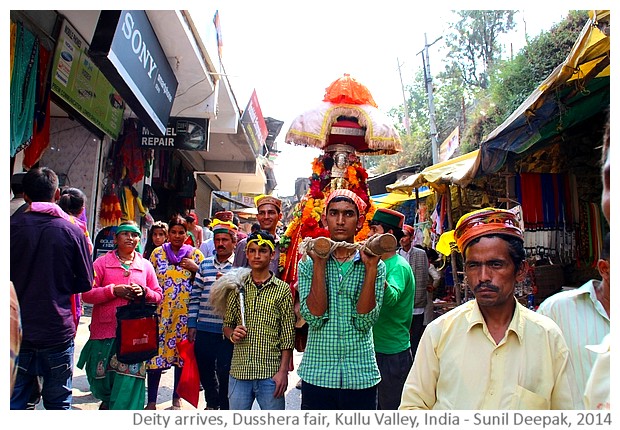
Garbhagriha (literally the Uterus, the most sacred part of the temple) hosting the sacred shrine to the goddess in an underground cave, has a black coloured sloping stone roof. It is at a lower level, and is the oldest and the most beautiful part of the temple. Its outer walls are covered by sculptures, some of them exquisitely carved into stone. The eastern wall of this building hosts a vermilion coloured Ganesha statue where pilgrims stop to pray and to try to affix a coin on its surface - if your coin sticks, it means that your wish will be granted.
The remaining three buildings are at entrance level so you do not need to negotiate any stairs. Beyond the main temple, up across some stairs, you can also visit a
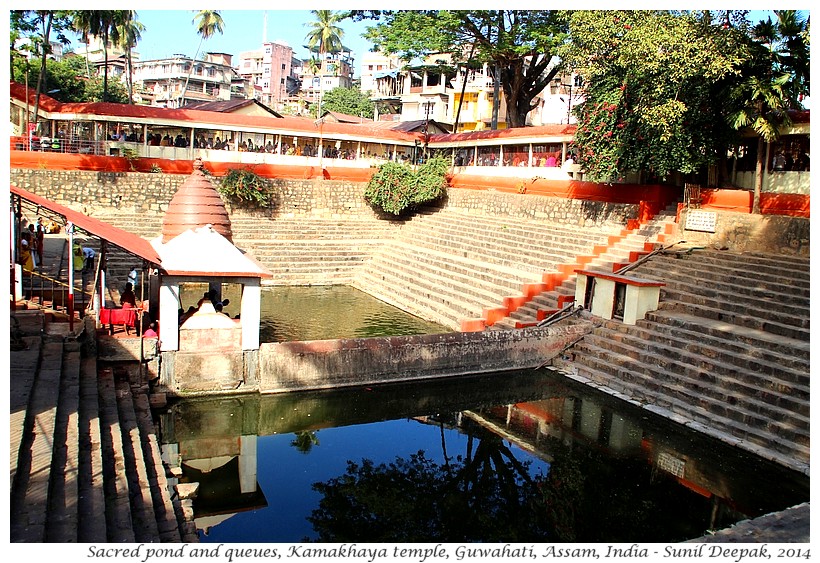
small sacred pond divided into 2 parts, with another small temple. Often people sit around on
the stairs for an overview of the temple complex.
The building at the western end is connected to a covered
passage going around the sacred pond, where persons wishing to visit the
Garbhagriha can wait in a queue. Persons willing to pay can enter the Garbhabriha from other entrances, without waiting in the long queue.

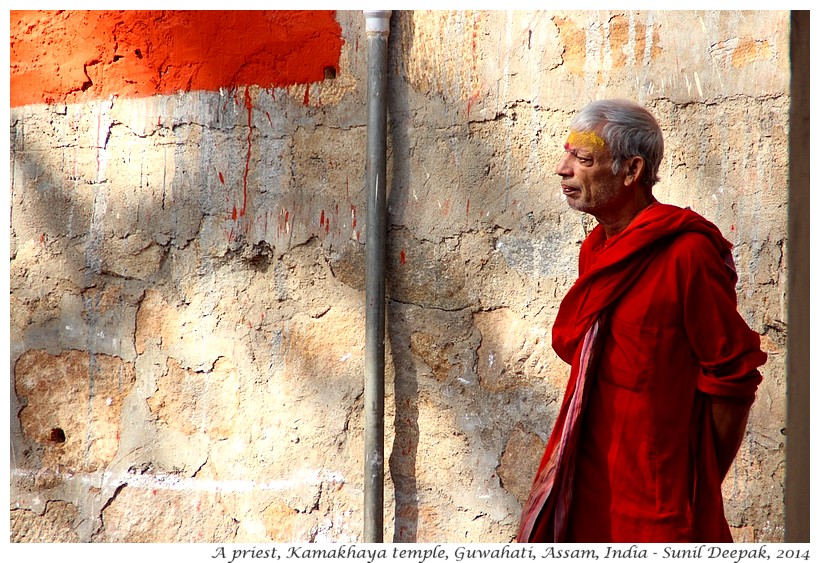
Brahmins dressed in red clothes wait all around the temple looking for clients for different religious ceremonies such as Shradha
(rituals for salvation of souls of dead family members) and
goat-sacrifice.
The monetary part of the temple visit and rituals can seem very
in-your-face, but if you are not in a hurry, you can focus on
appreciating the spiritual aspect of Shakti-worship.


Visiting the Garbhagriha: The underground cave of Garbhagriha can be visited only by Hindus. Even if you do not wish to visit it,
you can still walk all around the temple, appreciate the different
prayer spots and temples located around, and may be, sit down at a calm
spot to meditate.
I did visit the Garbhagriha of Kamakhaya temple once, a few
years ago. A narrow dark path cut into a rock takes you down to a cave,
where a small spring bathes a yoni (vagina) shaped rock surface.
The water of the spring, naturally mixed with an iron compound, and has a
blood like red tinge. Thus the journey to the inner sanctum can be
seen as a metaphorical journey back to the womb of the mother goddess,
followed by rebirth.
I am claustrophobic, and thus
found the walk through the narrow rocky passage a little terrifying. I
remember the darkness on the stairs, persons behind pushing, kneeling down in a dark barely lit cave, quickly touching the wet stone while a priest had chanted some mantra and given me a
spoon of that water to drink. It was all
over in a few minutes.
I know persons who find spirituality in the experience of visiting the underground cave. I did not have any such feelings.
Shoes and cameras: Outside the temple, you need to remove your shoes. You can leave them with one of the shops near the temple gate for a few rupees. However, on festival days when it can be very crowded, it will be better to leave your shoes away from the temple and walk bare feet, since finding a safe place near the temple is difficult.
Unfortunately the management board of this famous temple has not made proper arrangements for collection of visitors' shoes and sometimes people can steal your shoes left outside (it happened to me the last time I was there - and there are no footwear shops on the hill!).
You can go inside the main temple gate with your camera, but you are not allowed to take any bags with you (not even the camera bags) – so make sure to leave your bags in some safe place before reaching the temple. Photography is possible everywhere in the outer areas of the temple but not in the inner parts and certainly not in the inner sanctum, Garbhagriha.
SCULPTURES OF KAMAKHAYA TEMPLE
An Assamese researcher Mousumi Deka has written a nice article about the sculptures of Kamakhaya temple (Sculptures of Kamakhaya temple: An aesthetic view, in International Journal of Scientific and Research Publications, Volume 3, October 2013).
Inside the temple, it is usually crowded and difficult to look at the statues properly. An opportunity to see some of the inner sculptures comes with annual Ambubashi festival when they are placed outside for worship (an example is in the image below).

Hinduism has 2 broad groups of worship-paths (along with innumerable lesser groups, each with its own philosophy and ideas that flow like streams into Hinduism) - Bhakti Marg or the path of devotion linked to Vaishnavism (cult of Vishnu); and the Tantrik marg or the path of rituals including sexual rituals and chanting of sacred words (mantra), linked to Shaivism (cult of Shiva). Kamakhaya temple is linked to the Tantrik path of worship.
The two paths, Bhakti and Tantrik, are not mutually exclusive - there is often intermingling between the two. Thus, Kamakhaya temple includes many references to Vaishnavism.
REACHING KAMAKHAYA TEMPLE
The temple is located near the top of Nilachal hill (Nil = Blue, Achal = immovable or mountain) in the south-eastern part of Guwahati, close to the southern bank of Brahmaputra river. You can start the walk at the base of the Nilachal hill, at a place called “Kamakhaya gate” on the A.T. Road, close to the Kamakhaya railway station (a small and new railway station; the main railway station of Guwahati is at Paltan Bazar, a few kilometres to the west).
Nilachal hill is supposed to be only 160 metres high and from the Kamakhaya gate, the temple is only 2 km away - yet it can be a difficult climb, especially on a hot and humid summer day. You can take a shared taxi from the gate to the temple. Another convenient option is to take the special Kamakhaya city bus near Nehru Park in Uzan Bazar, not far from the main Guwahati railway station.
There many other temples on Nilachal hill, on the way to Kamakhaya. Thus, after the Kamakhaya visit, you can walk down to visit them. This will also give you an opportunity to look at the green hills surrounding Guwahati and have panoramic views of the city.
MYTHS AND STORIES RELATED TO NILACHAL HILL & KAMAKHAYA TEMPLE
Hinduism brings together different streams of ideas, stories and philosophies, including those that are clearly contradictory. One such dominant stream of ideas is linked to the figure of Shiva, the god of death and destruction. Shiva is also Neelkantha, the god with a blue throat (blue is a poison of the world that Shiva holds in his throat to safeguard the universe). Shiva’s abode is in Himalayan mountains. His consort Shakti (Power), also known as Gauri, Sati or Parvati, is the daughter of Himalaya. While snakes (Nag) live wrapped around Shiva's neck, his companions include the Naga people. Thus, Shiva and Shakti represent the culture of north-east mountains in Hinduism. Nilachal hill, or the blue hill, represents Shiva himself.
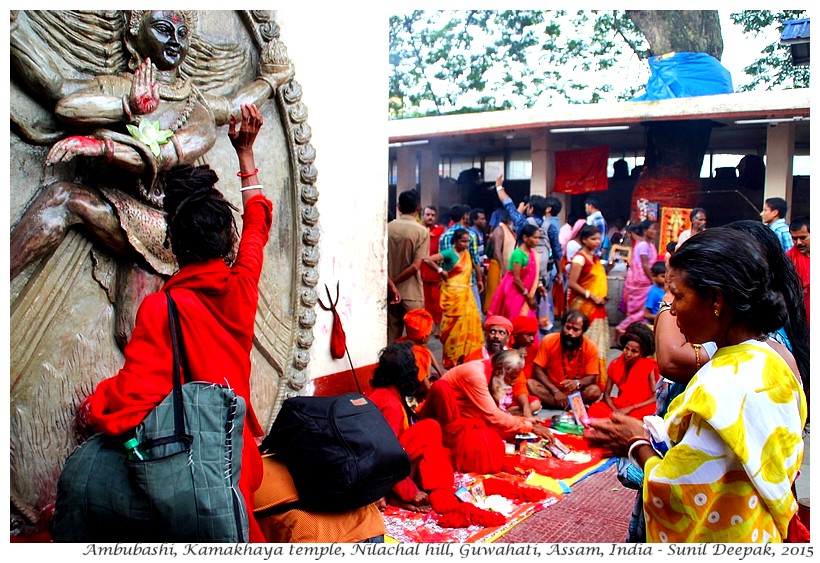

Shiva and Shakti cults are very strong in the north-east. These cults revolve mainly around phallus (Shiva linga) but occasionally, also around the female genitals (Yoni), and celebrate sexuality as a primordial creative force of nature.
Shakti cults are about different forms of feminine powers – as mother, as fighter, as giver of wealth, as protector of knowledge, as giver of joy, and as the face of destruction. The North-east of India has a rich calendar of festivals linked to the celebration of different forms of Shakti - such as the festivals of Kali, Durga and Saraswati.
Goddess Kamakhaya of Guwahati is another form of Shakti that links to the female sexuality and fertility. One of the stories of Kamakhaya is about Sati, the daughter of Himalaya and Shiva’s wife.
Story of Sati and Shiva: Sati was the daughter of the mountain king Daksh. She fell in love with Shiva, whose followers were drunkards, pot-smokers and an unruly lot. Daksh did not like Shiva but Sati insisted on getting married to him. Once Daksh organized an important religious ceremony but did not invite his son-in-law. Sati angry with her father, decided to commit suicide by jumping in the sacred fires. Shiva grief stricken, first destroyed the mountains and then, holding his wife’s dead body, wandered all over the land. Parts of dead Sati’s body fell away during these wanderings. Her yoni (genitals) fell on Nilachal hill, where the Kamakhaya temple was built.
According to the other stories, Nilachal hill is the site where Shiva mates with his consort, Shakti. Thus Kamakhaya temple celebrates the sexual union of Shiva and Shakti, and is considered an ideal place for pursuing Tantrik powers.
There are other myths and stories linked to Nilachal hills, such as the stories of Narakasur and the stories of the love-god, Kamadev.
The Narakasur stories are about an Asur king who lived in this region. He fell in love with princess Kamakhaya of Nilachal hills and wanted to marry her. The princess did not want to marry him but did not wish to offend him. So she laid down her condition: “Make steps from the base of the hill to the top in one night and I will marry you”. Narakasur used all his strength to make the steps and was making very good progress. The princess was afraid that he would finish them and marry her, so decided to play a trick. She asked a rooster to start crowing. Naraksur, when he heard the rooster, thought that it was already morning and that he had not been able to fulfil princess’ condition, gave up. BTW, there are unfinished steps near Kamakhaya that are shown to the tourists as the proof for this story.
The Kamadev stories: Kamadev is the god of love in Hinduism. His name literally means the "god of desire". In the stories, he is accompanied by his consort Rati (sexuality) and a friend, Vasant, the goddess of spring. Kamadev was supposed to be born on the Nilachal hill and gave the old name of "Kamrup" to Guwahati. Still today, the district of which Guwahati is a part, is called Kamrup.
The ancient myths of female sexuality related to Kamakhaya are omnipresent in some present-day beliefs where the women of the north-east region of India are sometimes described as “magicians” who can turn stranger men into sheep and keep them as their slaves, not letting them go back to their homes.
KAMAKHAYA TEMPLE
A wooden passage connects the Kamakhaya parking place/bus stop to the path going towards the temple. The whole passage is also lined with shops selling prayer materials and other trinkets. Along the passage sit many sadhu (ascetics in orange clothes) and beggars, who usually ask for alms from persons coming back from the temple visit.
The temple is placed along an east-to-west axis, starting with the
Garbhagriha near the gate, followed by other three inter-connected
buildings. The fourth building is the site for the animal sacrifices
(black goats). The image below has been taken from the western end and shows the first 3 buildings of the temple.
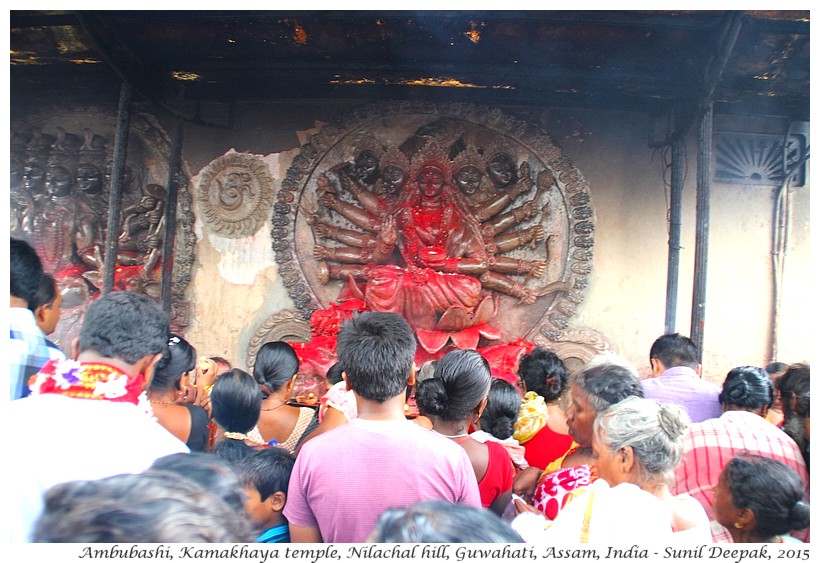

The sculptures on the external walls can be divided into 4 groups - sacred figures, daily life figures, plants and animal figures and geometric designs. Many sacred sculptures are in eastern style found in eastern part of India (in the states of Odisha, Bengal and Assam).
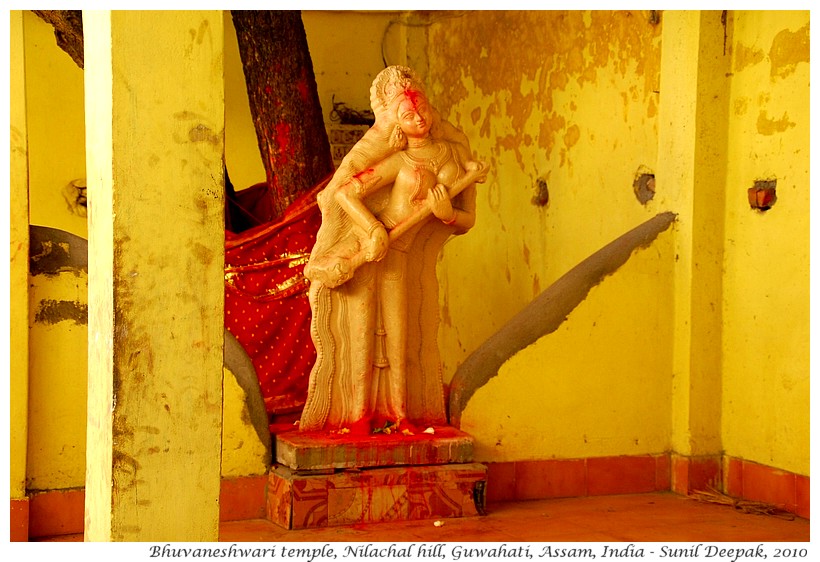
The male sacred figures include different representations of Shiva, especially those in which he is shown as the destroyer of the world (Bhairava). The female sacred figures are different representations of Shakti – such as Gauri (nubile girl), Uma (an adolescent girl becoming aware of her own body and its desires, symbolized by a hand-held mirror), Bhuvaneshwari holding a Veena (a music instrument) in her hands and as Kamakhaya (a woman in control of her sexuality).
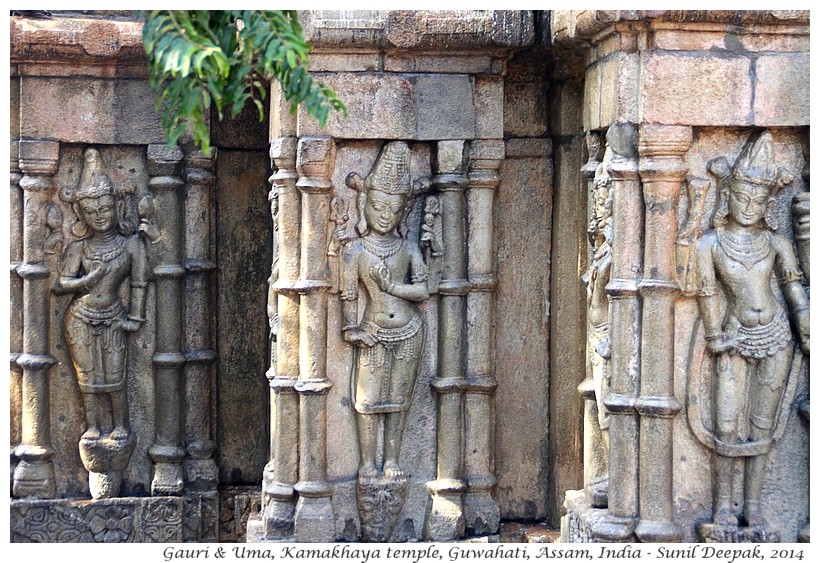
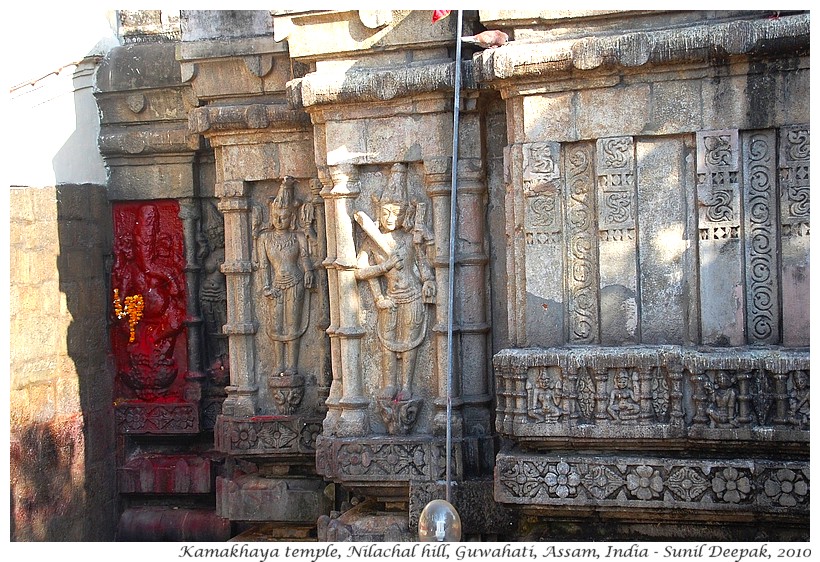


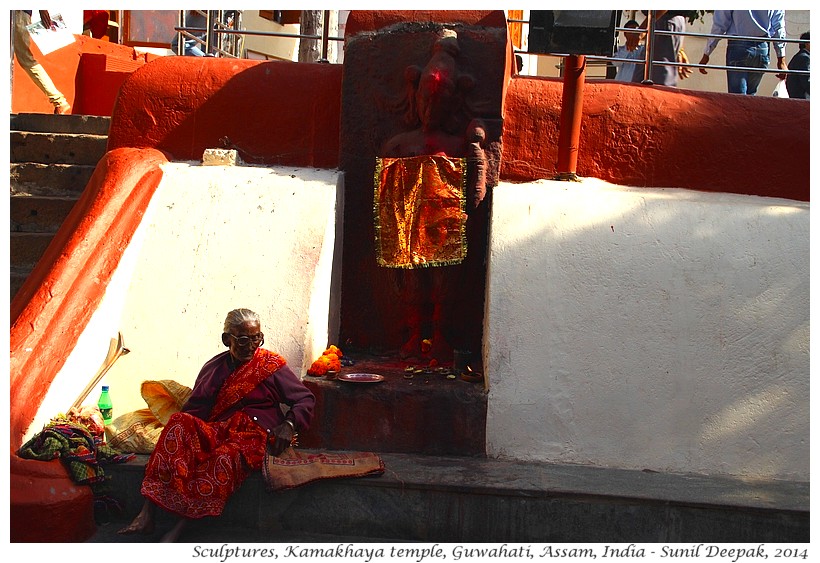
Sculptures with Kamakhaya representations where the goddess freely expresses her sexuality, are sometimes partly covered (like in the image below).

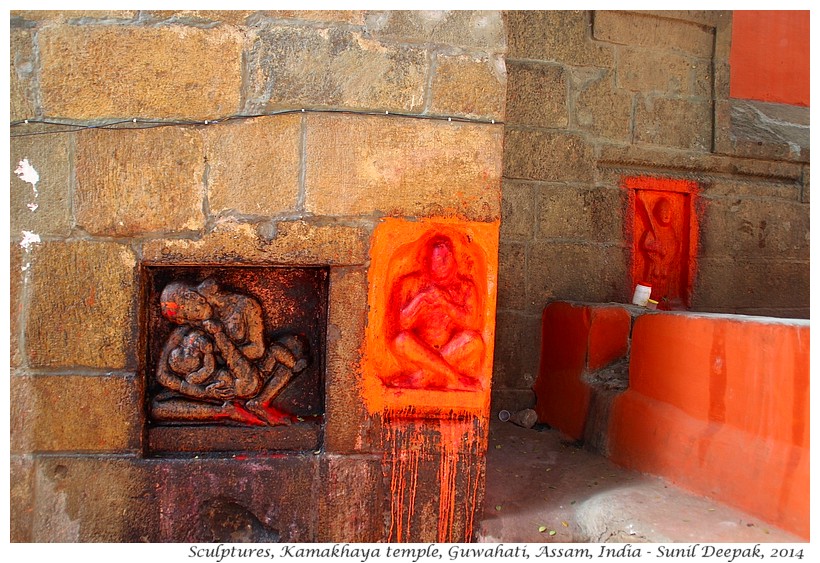
The sculptures representing daily life include a beautiful depiction of a mother breast feeding her baby (in the image below).

AMBUBASHI FESTIVAL
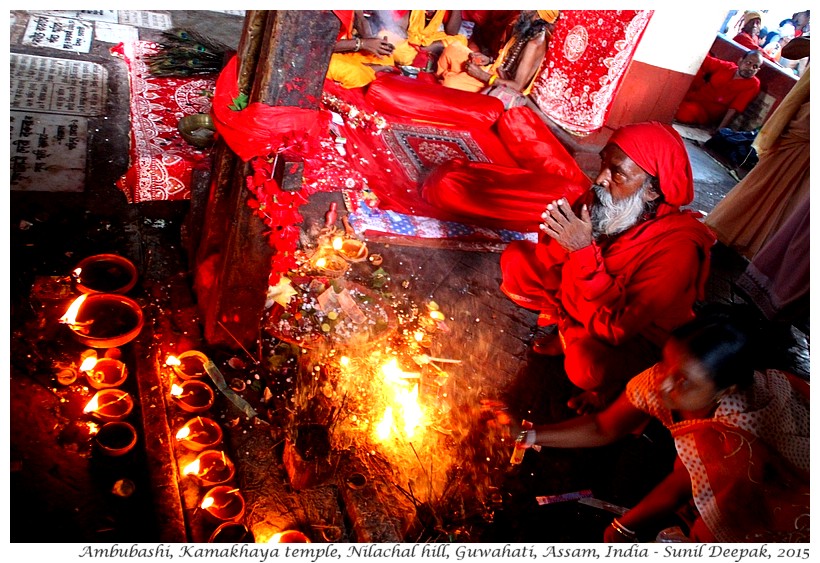
The annual Ambubashi festival is celebrated in June and usually coincides with the arrival of the monsoon rains. This festival celebrates the menstruation of Kamakhaya and the renewal of her fertility cycle. For three days the doors of Garbhagriha are closed while huge crowds of persons gather outside the temple to sing, dance and pray. On the fourth day when the temple doors are opened, there are huge crowds to visit and pray to the goddess.
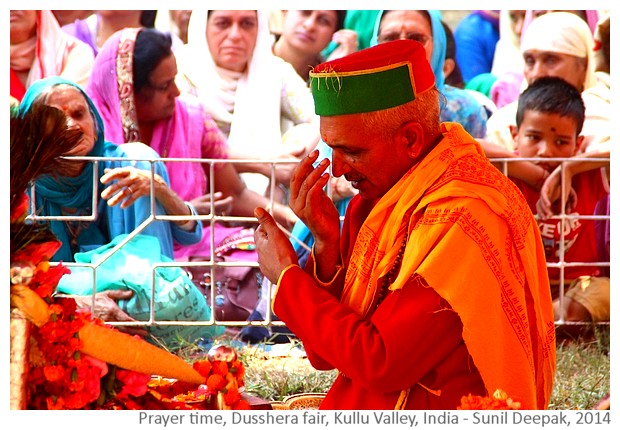
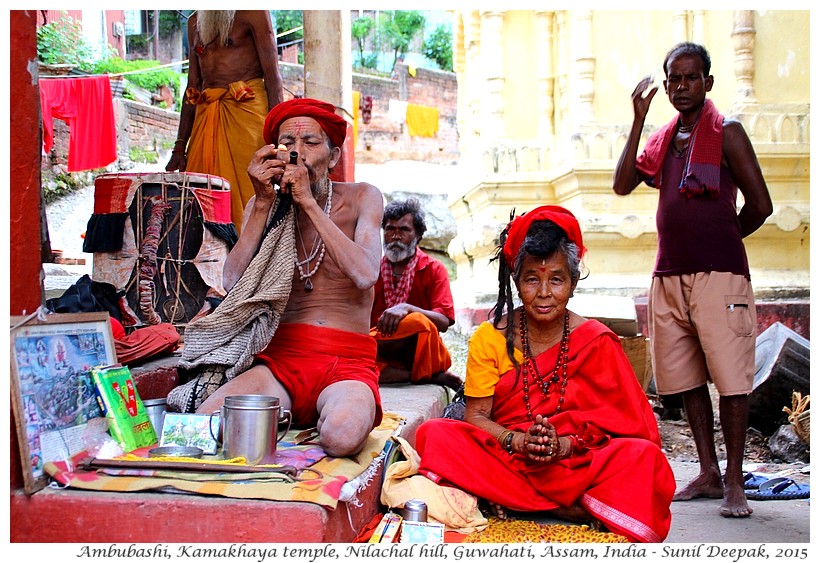
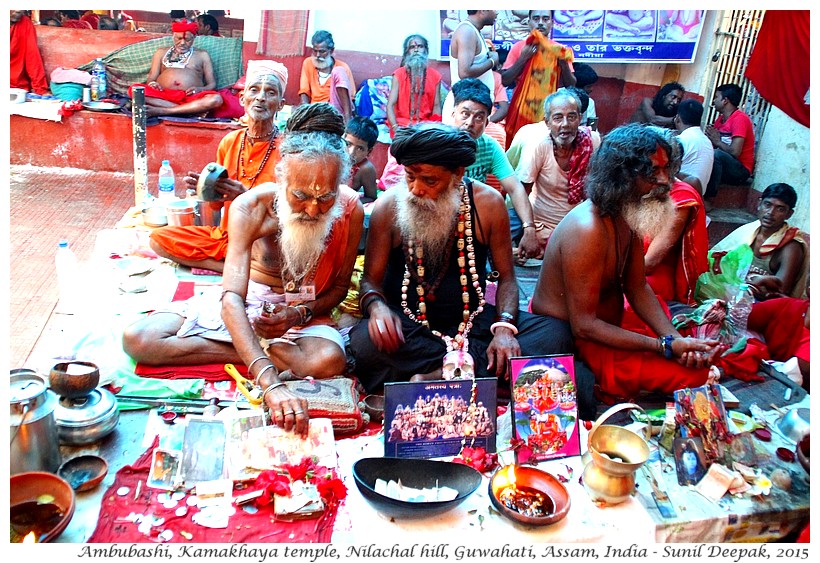
Ambubashi period is considered especially important for those who believe in Tantrik way of worship. Thus, tantrik sadhu (ascetics, wearing orange or red or black clothes) come out from their isolation in the mountains to visit the temple and to conduct special prayer ceremonies (in the image below).

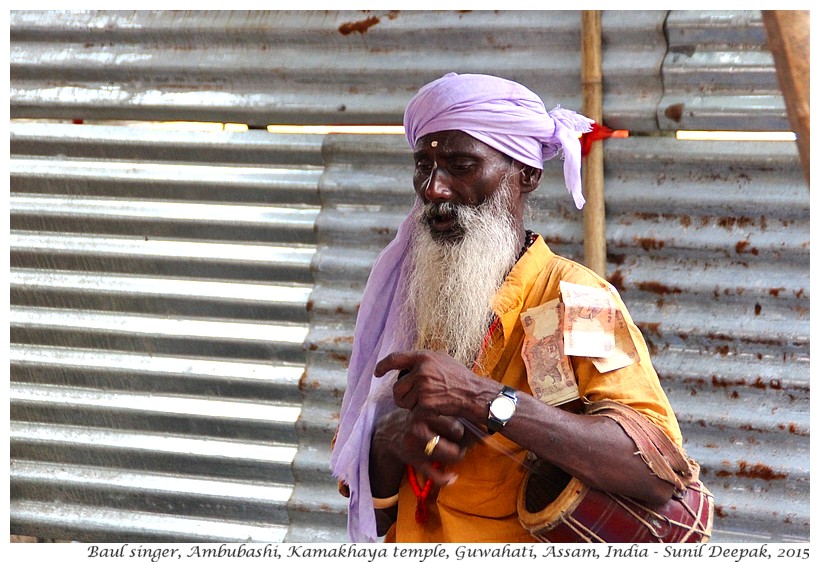
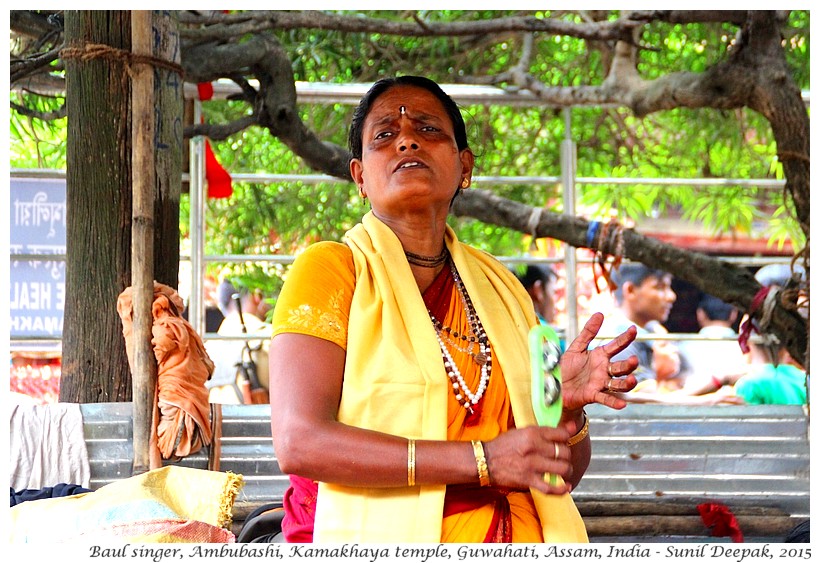
Baul singers who are wandering minstrels, singing about love of nature, freedom and humanity, represent a syncretic tradition of the north-east. They include Vaishnav Hindu sadhu and Muslim Sufi saints, and are a very heterogeneous group. Groups of Bauls also gather at Kamakhaya during the Ambubashi time (two Baul singers in the images below).


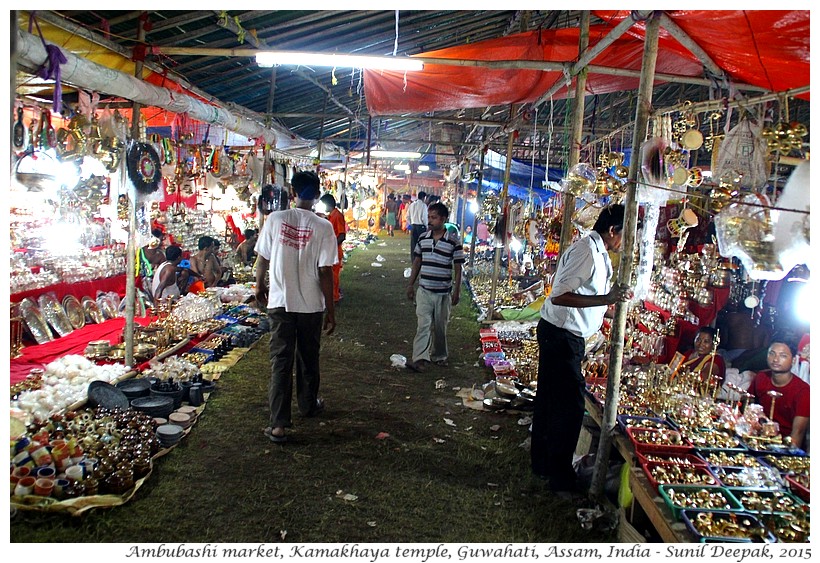
Thousands of pilgrims come to Guwahati for Ambubashi and the government organises free camps to host them. Free transport is also organised for pilgrims from Kamakhaya gate to the temple. A huge fair with hundreds of village shops is held near Kamakhaya temple on this occasion.

Though Guwahati can be impossibly hot and humid in that period, Ambubashi is one of the best times to visit Kamakhaya temple and Nilachal hill. Personally, I think that the opportunity to listen to the different Baul singers lost in their mystic trance is the best part of Ambubashi.
OTHER PLACES TO VISIT ON NILACHAL HILL
Nilachal hill has five Shiva temples – Siddheshwar, Kameshwar, Kotilinga, Aghor and Amratkeswar.
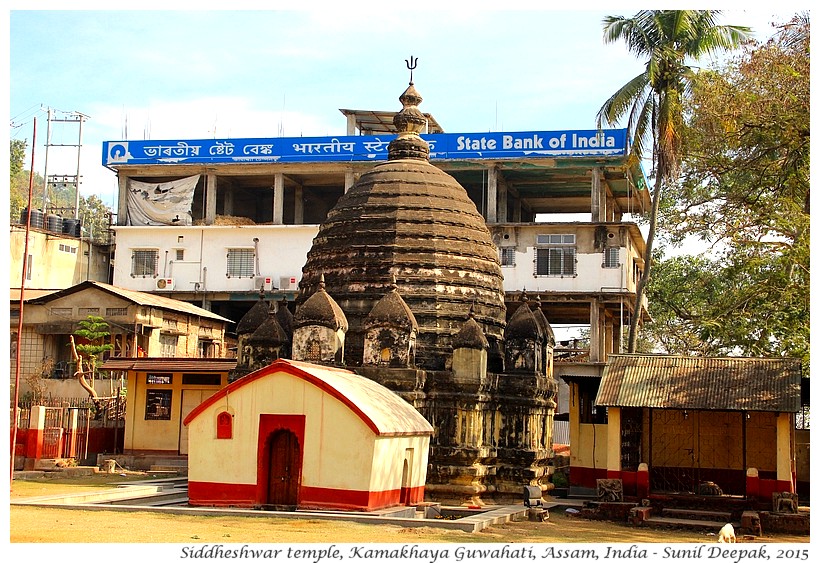
Siddheshawar temple in front of the parking place of Kamakhaya is one of the ancient temples of this region. It has some beautiful sculptures, probably dating back to medieval period. This temple is under Archaeological Survey of India. Unfortunately there are uncontrolled constructions all around this temple, that tower above the temple and deface its ancient beauty.
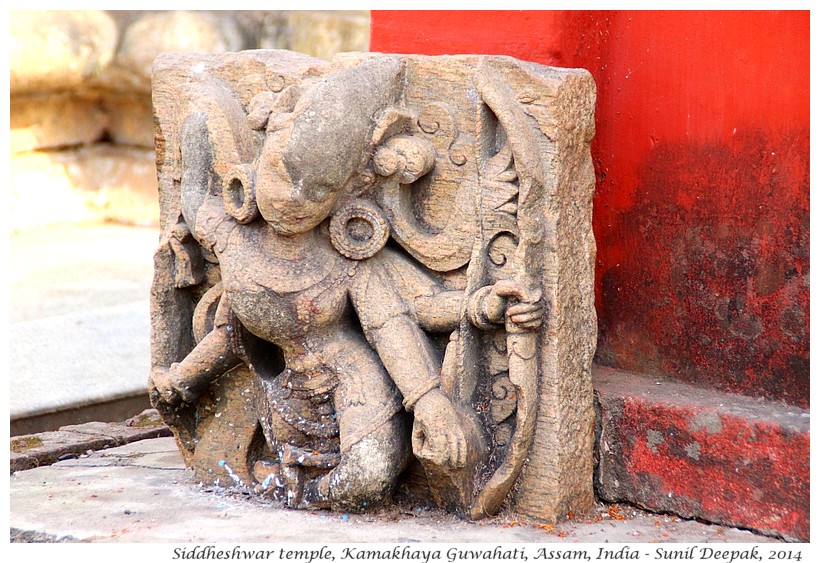


Tara temple with stairs going up near the entry gate of Kamakhaya temple is another small, but beautiful ancient building. As with Siddheshwara temple, here also uncontrolled constructions of multi-story concrete buildings around the temple, disturb its ambiance.
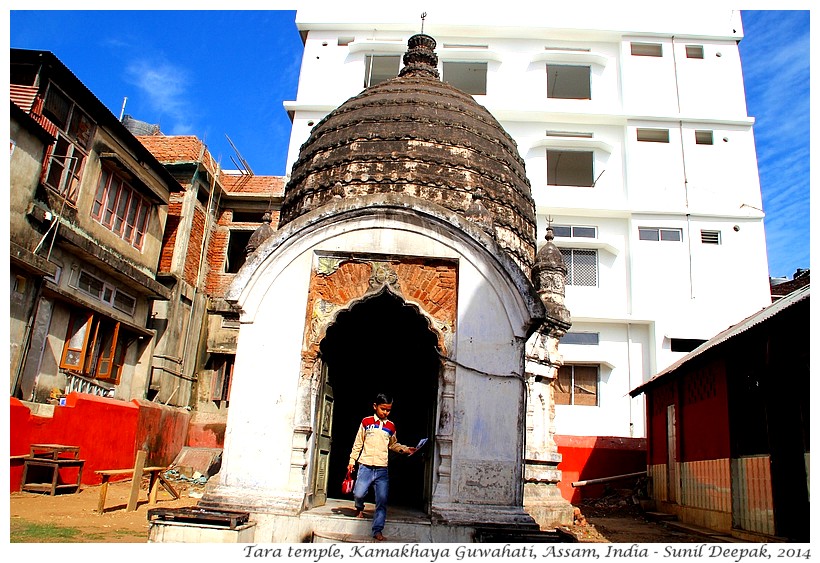

Bhairava temple near the base of Nilachal hill and Bagala temple near Kamakhaya are both known for their importance in Tantrik worship. If you follow the main road going up beyond the Kamakhaya temple, you can see the entrance to the Bagala temple.
If you will continue climbing the hill beyond Bagala temple, you will reach the top of Nilachal hill with the Bhuvaneshwari temple.

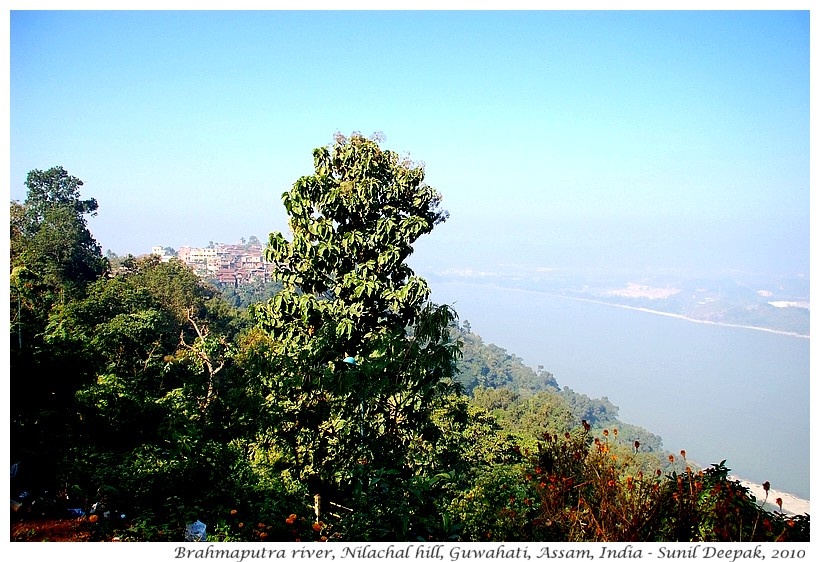
From here you can see a panorama of Guwahati city as well as the river Brahmaputra with its white sandy beaches below the hill. Across the river, on the other side, on a clear day you can also see the new buildings of Guwahati IIT.

CONCLUSIONS
Hiking up from the base of the Nilachal hill to Kamakhaya temple requires stamina and preparation. It is easier to take a state bus or a shared taxi to the temple and then walk around. However, at the end of the visit you can walk down and visit the other temples that line this road.
I like this tradition of acknowledging and respecting the female sexuality of Kamakhaya. This walk is a great way to understand and appreciate some of the complexities of Hinduism.

Unfortunately the management of Kamakhaya temple has not been able to provide basic services like a proper place for depositing shoes and bags. Even worse, uncontrolled constructions have spoiled many of the ancient temples near Kamakhaya.
Not withstanding this neglect, it is the simple faith of sadhus, Baul singers and ordinary pilgrims from far away places that will touch your heart during the Kamakhaya visit, especially during the annual Ambubashi festival.
***